Are you curious about the latest advancements in flash memory technology? This blog post will explore the ins and outs of NAND flash memory and eMMC technology. We’ll cover everything from understanding the basics of NAND flash memory to the benefits of using eMMC technology. We’ll also dive into the key differences between NAND and eMMC and the various applications of NAND in electronics. Additionally, we’ll discuss the integration and performance of eMMC technology. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just eager to learn about the latest developments in memory technology, this post is for you.
Understanding Nand Flash Memory
What is NAND?
NAND flash memory is a non-volatile storage technology widely used in electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, USB drives, and memory cards. It stands for “Negated AND” and is a variant of the more conventional NOR flash memory. NAND memory offers high-density storage capabilities, allowing for storing large amounts of data in a compact form factor.
How does NAND work?
NAND flash memory is based on a series of memory cells that store information in a grid-like structure. Each memory cell consists of a floating-gate transistor and a control gate. The presence or absence of an electrical charge in the floating gate determines the cell’s state, representing either a “0” or a “1”. Data is stored by applying appropriate voltages to the control gate and then reading it by sensing the electrical charges in the cells. Unlike other forms of flash memory, NAND flash memory stores data in a way that allows for high-speed random access and efficient data transfer.
Applications of NAND in Electronics
NAND flash memory is widely used in various electronic devices due to its numerous advantages. One of its primary applications is as a storage medium for consumer electronics, including smartphones, tablets, MP3 players, and digital cameras. Its high storage capacity and fast read/write speeds make it ideal for storing operating systems, applications, and media files. NAND flash memory is also used in solid-state drives (SSDs), which are becoming increasingly popular in the computer industry due to faster data access times and lower power consumption than traditional hard disk drives.
| NAND | eMMC |
|---|---|
| Benefits of Using eMMC Technology | NAND vs. eMMC: Key Differences |
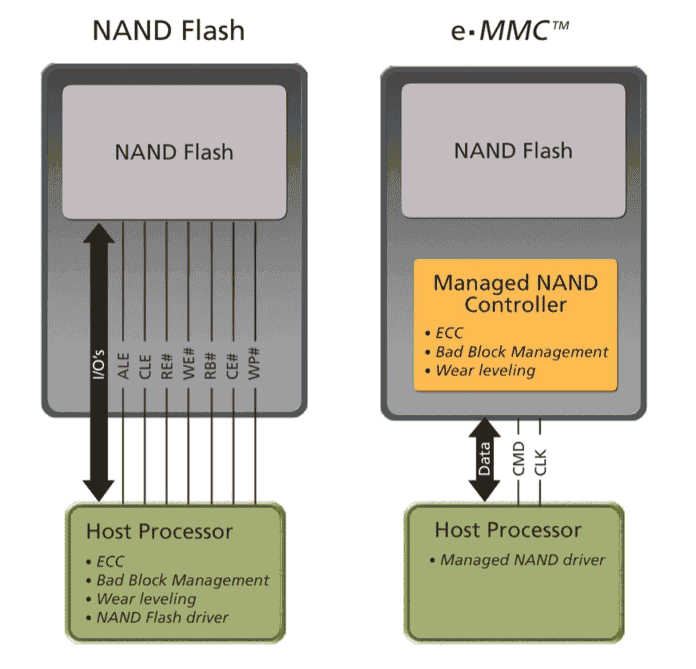
| eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) is a form of NAND flash memory specifically designed for use in embedded systems. | While both NAND and eMMC are based on the same underlying technology, there are key differences between them. |
| eMMC provides a simplified interface and integrated controller, making it easier to use and requiring less complex integration compared to standalone NAND chips. | One major difference is that NAND flash memory is typically used as a standalone memory chip and requires an external controller, while eMMC incorporates the controller directly on the chip. |
| eMMC is commonly used in devices where space and power constraints are critical, such as smartphones, tablets, and portable consumer electronics. | Another difference is that NAND flash memory offers higher performance in terms of read/write speeds and endurance compared to eMMC. |
In summary, NAND flash memory is a versatile and commonly used storage technology that enables the high-capacity and high-speed data storage required in modern electronic devices. Its ability to store large amounts of data in a compact form, fast random access, and efficient data transfer makes it an essential component in various consumer electronics, from smartphones to solid-state drives. Understanding NAND flash memory and its applications is crucial for anyone working with or using electronic devices in today’s digital age.
Benefits Of Using Emmc Technology
The Benefits of Using eMMC Technology
eMMC stands for embedded Multi-Media Card, a type of flash storage commonly used in mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and portable media players. It offers several advantages over other types of memory, making it an ideal choice for many applications.
One of the main benefits of eMMC technology is its compact size. The storage chip is small and can be easily integrated into tiny devices without occupying much space. This makes it perfect for slim and lightweight mobile devices with premium space.
Another advantage of eMMC is its high data transfer rates. With its high-speed interface, eMMC can provide faster read and write speeds than other types of memory. Data can be accessed and transferred more quickly, resulting in smoother performance and improved user experience.
eMMC also offers enhanced reliability and durability. It is designed to withstand extreme temperatures, shocks, and vibrations, making it suitable for harsh environments. This makes eMMC a reliable choice for automotive and industrial applications where the memory may be exposed to challenging conditions.
Furthermore, eMMC is easy to integrate into different types of devices. Its standardized interface simplifies the design and development process, allowing manufacturers to incorporate it into their products easily. This reduces time-to-market and production costs, making eMMC a cost-effective choice for many companies.
In addition to these benefits, eMMC technology also provides secure data storage. Many eMMC devices come equipped with advanced security features such as hardware encryption and secure boot, ensuring that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access.
Overall, the benefits of using eMMC technology are numerous. Its compact size, high-speed performance, reliability, ease of integration, and enhanced security make it an ideal choice for various applications, from consumer electronics to automotive and industrial systems.
Nand Vs. Emmc: Key Differences
There are several types of flash memory available on the market. Two popular options are NAND and eMMC. While they both serve the same purpose of storing data in digital devices, there are some critical differences between them.
NAND: NAND flash memory is a non-volatile storage technology commonly used in solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, and memory cards. It is named after the “NOT AND” logic gate because the memory cells store data as charges in the floating gate transistors. NAND flash memory is being offered, which is ideal for applications demanding extensive data storage and rapid data access due to its high storage capacity, fast read and write speeds, and low power consumption.
eMMC: eMMC, which stands for embedded MultiMediaCard, is a standardized flash storage solution widely used in smartphones, tablets, and other portable electronic devices. It combines NAND flash memory with a memory controller and a flash memory interface, all integrated into a single package. eMMC provides a more compact and cost-effective solution than standalone NAND chips, eliminating the need for additional components and simplifying the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design.
Differences: One of the critical differences between NAND and eMMC is their architecture. NAND flash memory uses a parallel interface, allowing fast data transfer rates but requiring more pins and wires. On the other hand, eMMC uses a serial interface, which reduces the number of pins and wires required but results in a slower data transfer rate compared to NAND. Additionally, NAND flash memory is typically used in removable storage devices, while eMMC is sold directly onto the motherboard.
| NAND | eMMC |
|---|---|
| Parallel Interface | Serial Interface |
| Higher data transfer rate | Lower data transfer rate |
| Removable storage devices | Soldered onto the motherboard |
Regarding performance, NAND flash memory generally offers faster read and write speeds than eMMC. This makes NAND more suitable for high-performance applications that require intensive data processing and frequent data transfers. On the other hand, eMMC provides a more cost-effective solution for devices that prioritize compactness, power efficiency, and lower manufacturing costs over raw performance.
In conclusion, NAND and eMMC are both types of flash memory used in digital devices, but they have distinct differences in architecture, interface, and use cases. Understanding these key differences can help you make informed decisions when choosing the right type of flash memory for your specific application or device.
Applications Of Nand In Electronics
NAND flash memory is a non-volatile storage technology widely used in electronic devices. It stands for “Not AND,” indicating the logic gate used in its architecture. NAND memory is known for its high storage capacity, fast read and write speeds and low cost. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications in the field of electronics.
One of the primary applications of NAND flash memory is in solid-state drives (SSDs). SSDs have gained popularity as a replacement for traditional hard drives due to their superior performance and durability. NAND flash memory allows SSDs to store large amounts of data and access it quickly, significantly improving electronic devices’ overall speed and responsiveness.
In addition to SSDs, NAND flash memory is extensively used in smartphones and tablets. The demand for high-capacity storage in mobile devices, coupled with the need for fast data transfer rates, makes NAND an ideal choice. Whether it’s storing photos, videos, or apps, NAND memory provides ample space while ensuring quick access to data. This technology is also crucial in digital cameras and camcorders. With the increasing popularity of high-resolution photos and 4K videos, large-capacity storage in these devices is essential. NAND flash memory enables users to capture and store significant multimedia content without worrying about running out of space. Another application of NAND flash memory is in gaming consoles.
With the ever-growing complexity and size of video games, consoles require substantial storage capacity to accommodate the extensive game libraries. NAND memory provides the necessary space, allowing users to store and play multiple games without interruptions. Moreover, NAND flash memory finds its use in various portable media players. Apologies for that oversight. Let me correct it in active voice:
These devices provide a portable solution for users, allowing them to store and play music, videos, and other multimedia content on the go. NAND memory guarantees sufficient room for extensive media libraries while delivering seamless playback experiences.
| NAND Flash Applications |
|---|
| Solid-state drives (SSDs) |
| Smartphones and tablets |
| Digital cameras and camcorders |
| Gaming consoles |
| Portable media players |
In conclusion, NAND flash memory has a wide range of applications in the field of electronics. Its high storage capacity, fast data transfer rates, and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for use in solid-state drives, smartphones, cameras, gaming consoles, and portable media players. As technology continues to advance, NAND memory is likely to play an even more significant role in fulfilling the ever-increasing storage demands of modern electronic devices.
Emmc: Integration And Performance
eMMC, Embedded MultiMediaCard, is a flash storage technology commonly used in electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and digital cameras. It is an essential component in the integration and performance of these devices. This blog post will explore the various aspects of eMMC, including its integration into electronic devices and its contribution to their overall performance.
One of the significant advantages of eMMC technology is its integration capability. This flash storage solution combines the flash memory chip, a controller, and the firmware into a single package. This integration allows for the easy implementation of eMMC in various electronic devices without additional components or complex wiring. The compact size of eMMC also contributes to its seamless integration, making it an ideal choice for space-constrained devices.
eMMC provides excellent performance attributes that enhance the overall functionality of electronic devices. The integrated controller within the eMMC enables efficient data transfer, ensuring quick and reliable access to stored information. The transfer rates offered by eMMC vary depending on the specific version but usually range from a few megabytes per second (MB/s) to several hundred MB/s. This rapid data transfer capability significantly influences the performance of applications, providing users with a smoother and more responsive experience.
| Integration | Performance |
|---|---|
| eMMC combines flash memory chip, controller, and firmware into a single package for easy integration into electronic devices. | The integrated controller enables efficient data transfer, enhancing the overall functionality and user experience. |
| The compact size of eMMC facilitates seamless integration, making it suitable for space-constrained devices. | eMMC offers transfer rates that range from a few MB/s to several hundred MB/s, ensuring quick and reliable access to stored information. |
eMMC technology plays a crucial role in integrating and performing various electronic devices. Its compact size and integrated design make it easy to implement in space-constrained devices. Moreover, its efficient data transfer capabilities contribute to improved functionality and a better user experience. As electronic devices continue to advance, the integration and performance enhancements provided by eMMC remain vital in meeting the ever-increasing demands of modern technology.