Table of Contents
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the need for high-speed and reliable storage solutions has become increasingly important. Solid State Drives (SSDs) have gained popularity for their superior performance and efficiency compared to traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). This blog post aims to provide an in-depth understanding of different types of SSDs, including SATA SSDs, M.2 SSDs, and NVMe SSDs. We will explore the advantages of NVMe SSDs, compare their speed and performance, and discuss how to choose the suitable SSD for your specific needs. Additionally, we will delve into the future trends in SSD technology, providing valuable insights for tech enthusiasts and consumers alike.
Sata Ssds
SATA (Serial ATA) stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment and is a standard interface for connecting storage devices to a computer system. Regarding SSDs (Solid State Drives), SATA SSDs are popular due to their affordability and compatibility. These drives use the SATA interface to transfer data between the SSD and the computer’s motherboard. With the advancements in SSD technology, SATA SSDs have evolved to offer improved performance and higher capacities, making them an excellent option for everyday computing needs.
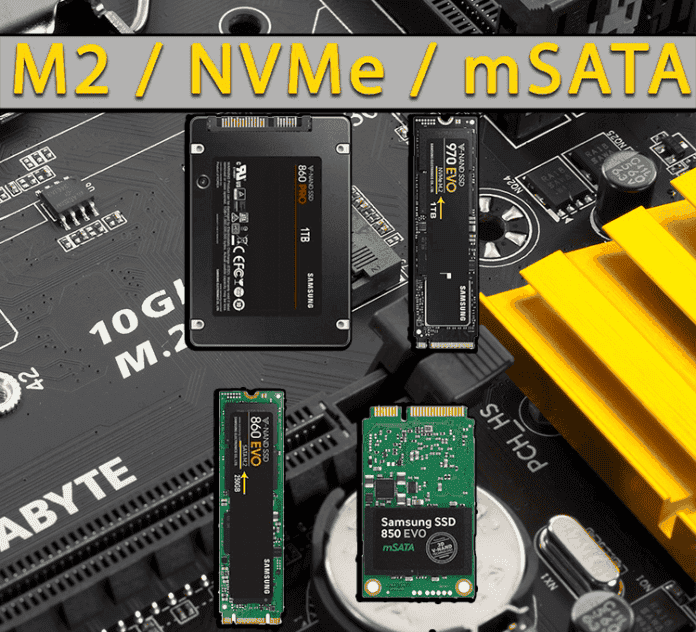
M.2, on the other hand, is a newer form factor for SSDs that offers significant advantages over traditional SATA SSDs. M.2 SSDs are smaller and connect directly to the motherboard using the M.2 slot. This eliminates the need for cables and allows for a more compact and streamlined system. M.2 SSDs also support faster data transfer speeds than SATA SSDs, making them ideal for demanding gaming and multimedia editing tasks. Additionally, M.2 SSDs can support both SATA and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) protocols, giving the user flexibility in choosing the type of SSD that best suits their needs.
NVMe is a protocol designed specifically for SSDs to exploit their low latency and high-performance capabilities. NVMe SSDs use the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface to communicate with the computer system, enabling faster data transfer rates and reducing processing overhead. This significantly improved speed and performance compared to SATA and M.2 SSDs. NVMe SSDs are commonly used in high-end applications with critical speed, such as data centers, professional workstations, and gaming systems.
- SATA (Serial ATA)
- M.2 (M.2 SSDs)
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express)
| Interface | Transfer Speed | Form Factor |
|---|---|---|
| SATA | Up to 6 Gbps | 2.5-inch |
| M.2 (SATA) | Up to 6 Gbps | M.2 form factor |
| M.2 (NVMe) | Up to 32 Gbps | M.2 form factor |
| NVMe (PCIe) | Up to 32 Gbps | Various form factors |
Introduction To M.2 Ssds
The emergence of M.2 solid-state drives (SSDs) has revolutionized the storage industry. M.2 SSDs are compact and provide blazing-fast performance, making them an ideal choice for modern computing devices. Compared to the more traditional Serial ATA (SATA) SSDs, M.2 SSDs offer several speed, size, and form advantages.
One of the critical advantages of M.2 SSDs is their smaller physical size. M.2 SSDs are much smaller than standard 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, making them ideal for small form factor devices such as ultrabooks and tablets. Their compact size allows more flexibility in designing slim, lightweight devices without compromising storage capacity or performance.
Another significant advantage of M.2 SSDs is their improved speed and performance. M.2 SSDs leverage the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) protocol, designed explicitly for solid-state storage devices. NVMe works directly over the PCIe bus, providing a faster and more efficient interface than the traditional SATA interface used by SATA SSDs. As a result, M.2 SSDs offer much higher sequential read and write speeds, leading to faster boot times and improved overall system responsiveness.
Advantages Of Nvme Ssds
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a cutting-edge interface protocol explicitly designed for solid-state drives (SSDs). It is geared towards optimizing the performance of SSDs by reducing latency and increasing bandwidth. The NVMe protocol is based on PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard. Unlike traditional SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) SSDs, which communicate with the computer system through a slower and older interface, NVMe SSDs use the PCIe connection to deliver exceptional speed and efficiency.
One of the significant advantages of NVMe SSDs is their incredible speed. By utilizing the PCIe interface’s high bandwidth and low latency, NVMe SSDs can offer significantly faster data transfer rates compared to SATA SSDs. This means that tasks such as booting up the operating system, loading applications, and transferring large files can be completed much more quickly. The improved speed of NVMe SSDs can significantly enhance overall system performance and productivity, especially in high-demand applications such as gaming, video editing, and data analysis.
| Advantages of NVMe SSDs | |
|---|---|
| 1. Enhanced Speed: | NVMe SSDs utilize the high bandwidth and low latency of the PCIe interface, resulting in significantly faster data transfer rates compared to SATA SSDs. |
| 2. Improved Responsiveness: | The low latency of NVMe SSDs reduces the time it takes for the system to access and retrieve data, resulting in faster application loading times and a more responsive computing experience. |
| 3. Increased Bandwidth: | NVMe SSDs have a greater bandwidth capacity, allowing for simultaneous data transfers and multi-threaded operations. This can lead to improved multitasking capabilities and smoother overall system performance. |
In addition to speed, NVMe SSDs also offer improved responsiveness. The low latency of NVMe SSDs reduces the time it takes for the system to access and retrieve data. This translates into faster application loading times, snappier file browsing, and a more responsive computing experience overall. Whether you’re launching a program, searching for files, or accessing data, the reduced latency of NVMe SSDs ensures that actions are completed without noticeable delays.
Furthermore, NVMe SSDs provide increased bandwidth compared to SATA SSDs. This allows for simultaneous data transfers and multi-threaded operations, improving multitasking capabilities and smoother overall system performance. With greater bandwidth, NVMe SSDs can handle multiple tasks concurrently, making them suitable for demanding workloads such as content creation, virtualization, and data centers.
Speed And Performance Comparison
Speed and performance are crucial factors when selecting the proper storage solution for your computer. This blog post will compare three popular storage technologies: SATA SSDs, M.2 SSDs, and NVMe SSDs. These three options offer varying performance levels, and understanding their differences can help you make an informed decision.
- SATA SSDs: SATA stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, and SATA SSDs have been widely used for many years. They are affordable and offer improved speed and performance compared to traditional hard drives. SATA SSDs use the SATA interface, limiting their maximum data transfer rate to around 600MB/s. While this is significantly faster than a hard drive, it falls short compared to the other options we will discuss.
| M.2 SSDs: | M.2 SSDs are a form factor for solid-state drives that connect directly to the motherboard. They come in different lengths and widths, denoted by numbers like 2230, 2242, 2260, and 2280. The M.2 interface supports both SATA and NVMe protocols, providing greater flexibility in terms of compatibility. While M.2 SATA SSDs offer similar speeds to traditional SATA SSDs, M.2 NVMe SSDs can deliver significantly faster performance. |
- NVMe SSDs: NVMe, which stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express, is an interface and storage protocol designed specifically for SSDs. NVMe SSDs use the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, allowing for much higher data transfer rates compared to SATA-based drives. With NVMe, sequential read and write speeds can reach several gigabytes per second, resulting in blazing-fast performance and reduced latency.
When comparing the three SSD technologies, it’s clear that NVMe SSDs offer the highest speed and performance. However, it’s important to note that not all systems support NVMe. Older motherboards may need more M.2 slots or have limited compatibility. Additionally, NVMe SSDs are more expensive than SATA and M.2 SATA counterparts.
In conclusion, if speed and performance are paramount, NVMe SSDs are the way to go. They offer unparalleled data transfer rates and can significantly enhance the overall responsiveness of your system. However, if your system cannot support NVMe or you’re on a budget, SATA SSDs or M.2 SATA SSDs are still excellent options that significantly improve over traditional hard drives. Consider your specific requirements and budget to choose the correct SSD.
Choosing The Right Ssd For Your Needs
When choosing the suitable SSD for your needs, several factors must be considered. One of the first decisions you’ll need to make is the form factor of the SSD. SATA SSDs and M.2 SSDs are two standard options in the market. SATA SSDs are the traditional 2.5-inch drives that connect to your computer using a SATA interface. They offer decent performance and are compatible with most computers. On the other hand, M.2 SSDs are much smaller and connect directly to your motherboard using the M.2 slot. They come in different lengths, the most common ones being 2242, 2260, and 2280.
One of the main advantages of M.2 SSDs is their smaller size. This makes them ideal for small form factor devices such as ultrabooks and mini PCs. Another advantage of M.2 SSDs is their speed. While SATA SSDs can reach around 550 MB/s, M.2 SSDs can achieve much higher speeds, especially if they support the NVMe protocol. NVMe stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express and is a faster interface for SSDs than SATA. SSDs that support NVMe can reach sequential read and write speeds of up to 3500 MB/s and 3000 MB/s, respectively.
When choosing the suitable SSD for your needs, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your use case. If you’re building a gaming PC or a high-performance workstation and need the fastest speeds possible, an M.2 NVMe SSD would be recommended. However, if you’re on a budget or have an older computer that only supports SATA, a SATA SSD would still provide a significant performance boost compared to a traditional hard drive. Additionally, consider the storage capacity you require. SSDs come in various capacities, from 128GB to terabytes, so choose one that can accommodate your files, programs, and operating system.
- In conclusion, choosing the right SSD for your needs involves considering factors such as form factor, speed, and storage capacity.
- If you require high speeds and have a compatible system, an M.2 NVMe SSD would offer the best performance.
- However, if you’re on a budget or have an older system, a SATA SSD can still provide a significant boost in performance compared to a traditional hard drive.
- Take into account your specific use case and storage requirements when making your decision.
| Factors to Consider | SATA SSDs | M.2 SSDs |
|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | 2.5-inch drive | M.2 slot on motherboard |
| Speed | Around 550 MB/s | Up to 3500 MB/s (with NVMe support) |
| Storage Capacity | Range from 128GB to terabytes | Range from 128GB to terabytes |
Future Trends In Ssd Technology
The future of SSD technology is promising, with several trends shaping the development and advancements in this field. One of the critical areas of focus is the interface. Traditional SSDs have primarily used the SATA interface, which is widely adopted and supported. However, with the growing demand for faster data transfer rates and higher performance, newer interfaces such as M.2 and NVMe are gaining popularity.
M.2 SSDs are smaller than traditional 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, making them ideal for compact, portable devices like laptops and ultrabooks. These SSDs use the M.2 form factor, allowing faster data transfer speeds. They can connect directly to the motherboard, eliminating the need for cables and reducing latency. M.2 SSDs also come in different sizes and critical configurations, providing flexibility and compatibility with various devices.
The emergence of NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs has revolutionized the storage landscape. Unlike SATA-based SSDs, NVMe SSDs communicate directly with the computer’s CPU through the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, resulting in breakneck data transfer speeds. This enables NVMe SSDs to deliver exceptional performance, making them the preferred choice for gamers, content creators, and professionals who require lightning-fast storage solutions.
- One of the significant advantages of NVMe SSDs is their low latency. With higher queue depths and more I/O operations per second (IOPS), NVMe SSDs can efficiently handle heavy workloads and deliver responsive performance.
- Another important trend in SSD technology is the increasing capacity of solid-state drives. As storage demands continue to grow, manufacturers are pushing the boundaries to offer larger SSD capacities. This allows users to store more data, whether it’s high-resolution videos, large software applications, or extensive multimedia libraries.
- Additionally, advancements in NAND flash memory technology, such as the transition from 3D NAND to 4D NAND, enable higher storage densities and improved reliability. These advancements contribute to the future development of SSDs with even larger capacities and enhanced endurance.
The future of SSD technology looks promising with the emergence of faster interfaces like M.2 and NVMe. As these technologies advance, we can expect even more excellent performance, increased capacity, and improved reliability from SSDs. Whether you’re a gamer, professional, or simply a tech enthusiast, keeping an eye on these future trends in SSD technology will help you stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of storage solutions.
| SATA SSDs | M.2 SSDs | NVMe SSDs |
|---|---|---|
| SATA interface | M.2 form factor | NVMe interface |
| Slower data transfer rates | Faster data transfer rates | Incredibly fast data transfer speeds |
| Widely adopted and supported | Smaller in size | Low latency and high performance |