Table of Contents
NFC technology, or Near Field Communication, has revolutionized daily interactions with digital devices. This powerful and versatile technology allows seamless connections between devices with a simple touch or a wave. From contactless payments and keyless entry systems to file sharing and intelligent posters, NFC has become integral to modern society. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the intricacies of NFC technology, exploring its uses, benefits, and future potential.
Evolution of NFC Technology: From Inception to Present
Near Field Communication (NFC) has come a long way since its inception, revolutionizing how we interact with devices and make transactions. The evolution of NFC technology can be traced through the following key stages:
- Invention and Early Development
The concept of NFC technology was first introduced in the 1980s, with the invention of RFID technology laying the groundwork for its development.
- Integration into Mobile Devices
One of the significant milestones in the evolution of NFC was its integration into mobile devices, allowing for seamless communication and data transfer.
- Expansion into Contactless Payments
NFC technology has revolutionized how we make payments, introducing contactless payment solutions that enable quick and secure transactions.
- Diversification of Applications
NFC technology is used for various applications, including access control, public transportation, and innovative city initiatives.
NFC technology’s evolution has shaped how we interact with the world around us, and its potential for future development is limitless.
Essential Components and Functionality of NFC
NFC technology, or Near Field Communication, is a wireless communication technology that allows for data transfer between two devices nearby. The critical components of NFC include an NFC tag, an NFC reader, and an antenna. The NFC tag contains the data to be transmitted while the NFC reader reads and processes the data. The antenna enables the communication between the two devices through electromagnetic induction.
Components of NFC Technology:
| Component | Functionality |
|---|---|
| NFC Tag | Stores and transmits data |
| NFC Reader | Reads and processes data |
| Antenna | Enables communication through electromagnetic induction |
NFC technology interacts with these critical components to facilitate seamless data transfer between devices, making it a versatile and convenient technology for various applications.
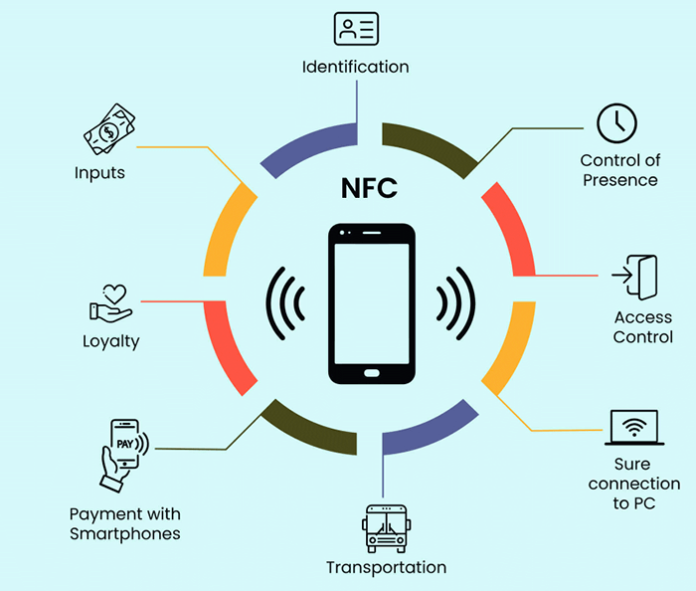
Applications of NFC Technology in Various Industries
NFC technology, or Near Field Communication, has emerged in various industries, revolutionizing business operations. From mobile payments and access control to supply chain management and marketing, NFC applications are numerous and diverse. In the retail sector, NFC technology enables seamless and secure transactions, while in healthcare, it facilitates patient identification and medication tracking. Furthermore, the transportation industry benefits from NFC technology through contactless ticketing and efficient logistics management.
The Impact on Retail
In the retail industry, NFC has transformed how customers make payments, allowing for quick and secure transactions with just a tap of their smartphone or card. This has led to a more convenient and streamlined shopping experience and improved customer satisfaction. Additionally, NFC tags can be used for product information and interactive marketing, enhancing the overall shopping experience for consumers.

Security and Privacy Considerations in NFC Technology
Near Field Communication (NFC) has revolutionized how we interact with our devices and make payments. However, with this convenience comes the need for robust security measures to protect user data and privacy.
Security Considerations
1. Data Encryption: All NFC transactions should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
2. Authentication: Implementing robust authentication protocols to verify the parties’ identity in the NFC transaction.
3. Secure Element: Utilizing a secure element to store sensitive data and perform cryptographic operations.
Privacy Considerations
1. Data Minimization: Limiting the amount of personal data exchanged during NFC transactions to minimize privacy risks.
2. Consent: Ensuring that users have control over their data and explicitly consent to NFC transactions.
3. Anonymity: Providing options for anonymous NFC transactions to protect user privacy.
By addressing these security and privacy considerations, NFC can continue enhancing user experiences while safeguarding sensitive information.
Future Trends and Innovations in NFC Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology looks promising. With the increasing demand for contactless solutions, NFC is expected to play a significant role in various retail, healthcare, and transportation industries. The emergence of wearables and IoT devices has also sparked new opportunities for NFC technology, paving the way for innovative applications and services. As the world becomes more interconnected, the future of NFC technology is bound to revolutionize how we interact with our environment.
The Impact of IoT and Wearables
One key driver of NFC innovation is the integration with IoT and wearables. With the rise of smart devices and connected ecosystems, NFC technology is poised to enable seamless communication and interaction between different devices. This opens many possibilities, from secure mobile payments to personalized user experiences. The combination of NFC, IoT, and wearables will drive the next wave of innovation, creating new opportunities for businesses and consumers.
Overall, the future of NFC-technology holds immense potential for shaping how we interact with digital and physical environments. As technology continues to mature and evolve, we expect to see exciting new applications and services that enhance users’ convenience, security, and connectivity worldwide.
Comparative Analysis of NFC-Technology with Other Wireless Communication Technologies
When it comes to wireless communication technologies, NFC (near-field communication) stands out as a promising option due to its unique features. Compared to other popular technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, NFC offers security, simplicity, and low power consumption.
Security
NFC technology provides a higher level of security than Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, as it requires devices to be close to establish a connection. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Simplicity
Unlike Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, NFC-technology enables seamless connectivity with a simple tap. This simplicity makes it ideal for quick and effortless data transfer and payment processes.
Low Power Consumption
NFC-technology is designed to operate with minimal power, making it ideal for various applications where energy efficiency is crucial. In contrast, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi consume more power, especially during data-intensive tasks.
| Comparison | NFC | Bluetooth | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | High | Medium | Medium |
| Simplicity | High | Medium | High |
| Power Consumption | Low | Medium | High |